By Kim Smiley
On July 25, 2012, an 11 year old boy managed to sneak aboard a flight to Rome from Manchester England without a ticket or a passport. No one noted the presence of the extra passenger until other passengers informed airline staff that the boy had told them he was running away from home and seemed suspicious. The timing of this incident was unfortunate since it occurred a few days before the start of the Olympics and raised more questions about British security.
How did a boy manage to depart on an aircraft without any of the proper documentation? This incident can be analyzed by building a Cause Map, a visual root cause analysis which intuitively shows the relationships between the causes that contributed to the issue.
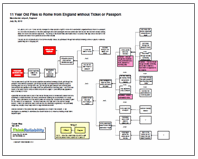 In this example, the boy was able to sneak onto the flight because the extra passenger wasn’t noted in the head count and he got through five separate security checks. The boy did not circumvent any of the normal security checks, he just walked through them without showing a shred of paper or anybody questioning him or stopping him.
In this example, the boy was able to sneak onto the flight because the extra passenger wasn’t noted in the head count and he got through five separate security checks. The boy did not circumvent any of the normal security checks, he just walked through them without showing a shred of paper or anybody questioning him or stopping him.
The boy was able to get into the secure departure area without showing a ticket, get through the passport check without a passport, get through security screening without showing a ticket or boarding pass (he did go through the x-ray), get through the gate passport and boarding pass check without any paperwork and finally board the plane without a boarding pass. Add in the final failure of the head count to notice an extra body and an English 11 year without any paperwork was on his way to Rome.
Apparently the boy was able to pull off this feat by sticking close to families with children and took advantage of situations where one family member was showing the documentation for a large group. Video surveillance from the airport shows him acting very confident and his behavior gave no one reason to be suspicious. The airport was also very busy due to the summer holiday season. Throw in an ineffective head count and the end result was a significant, if not particularly dangerous, security breach days before a huge international event.
Several members of the airline staff were suspended as a result of this incident. A full investigation is underway to understand the incident and work to ensure something similar never happens again.
To view a high level Cause Map of this incident, click on “Download PDF” above.