On February 9, 2009, a fire and explosion in a seriously overcrowded prison in Honduras resulted in 103 deaths and 25 injuries. The fire was started from a short circuit from a overheated refrigerator motor, used to store soft drinks for the inmates. The cell block – which has a capacity of 800 – contained 1960 inmates, their clothing, and their bedding materials. This provided plenty of fuel for the fire.
We can look at the causes that led to the prisoner deaths in a Cause Map, or visual root cause analysis. We begin with the impacts to the goals. The deaths and injuries of prisoners are an impact to the safety goal. The environmental goal was impacted by the severe prison fire and explosion. The customer service goal (considering the general population as the “customer” of a government-run prison) was unaffected, as there were no prisoner escapes. Finally, the property goal was impacted due to damage to the prison.
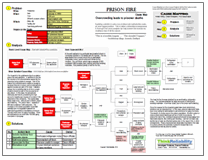 We can continue the Cause Map by asking “why” questions. The impacts to the goals were due to a severe prison fire and explosion. In addition to the fire, the injuries to the prisoners was caused by the prisoners being unable to escape. Part of the reason the prisoners were unable to escape is because they are in prison, and so precautions against escape are part of the deal. However, egress from a building that is on fire to a safe location should be part of the procedures of any prison. In this case, the procedures obviously didn’t work considering the high amount of deaths and injuries (of a total of 186 prisoners in this cell block). The egress was likely made more difficult due to severe prison overcrowding. The prison has a capacity of 800 and contained 1,960 prisoners. The increase in the prison population is at least partially due to a legislation passed the previous August which mandated a minimum 12-year prison term for gang members. There are estimated to be more than 100,000 gang members in Honduras.
We can continue the Cause Map by asking “why” questions. The impacts to the goals were due to a severe prison fire and explosion. In addition to the fire, the injuries to the prisoners was caused by the prisoners being unable to escape. Part of the reason the prisoners were unable to escape is because they are in prison, and so precautions against escape are part of the deal. However, egress from a building that is on fire to a safe location should be part of the procedures of any prison. In this case, the procedures obviously didn’t work considering the high amount of deaths and injuries (of a total of 186 prisoners in this cell block). The egress was likely made more difficult due to severe prison overcrowding. The prison has a capacity of 800 and contained 1,960 prisoners. The increase in the prison population is at least partially due to a legislation passed the previous August which mandated a minimum 12-year prison term for gang members. There are estimated to be more than 100,000 gang members in Honduras.
The heat for the fire was provided by an overheating refrigerator motor. The fuel was provided by large amounts of clothing and bedding materials – more than usual, due to the prison overcrowding.
Once the causes for the impacted goals have been determined, solutions can be brainstormed. In this case, prisoner advocates have been long calling for alternatives to jail sentences for gang members. This would, of course, reduce the prison population. Another option to reduce prison overcrowding would be to build more prisons. To reduce the risk of fire, motorized equipment should be kept away from flammable objects, like clothing and bedding. Last but not least, any facility has to have an effective egress plan in the case of fire or other emergencies. These procedures are especially important in the case of a prison, where the potential of prisoner escape has to be considered as well as prisoner safety.
To view the root cause analysis investigation, please click “Download PDF” above. Or click here to read more.
